Does Removing Product Increase Reaction Rate
Greater surface area of the jar C. The velocity of the reaction depends on activator concentration.
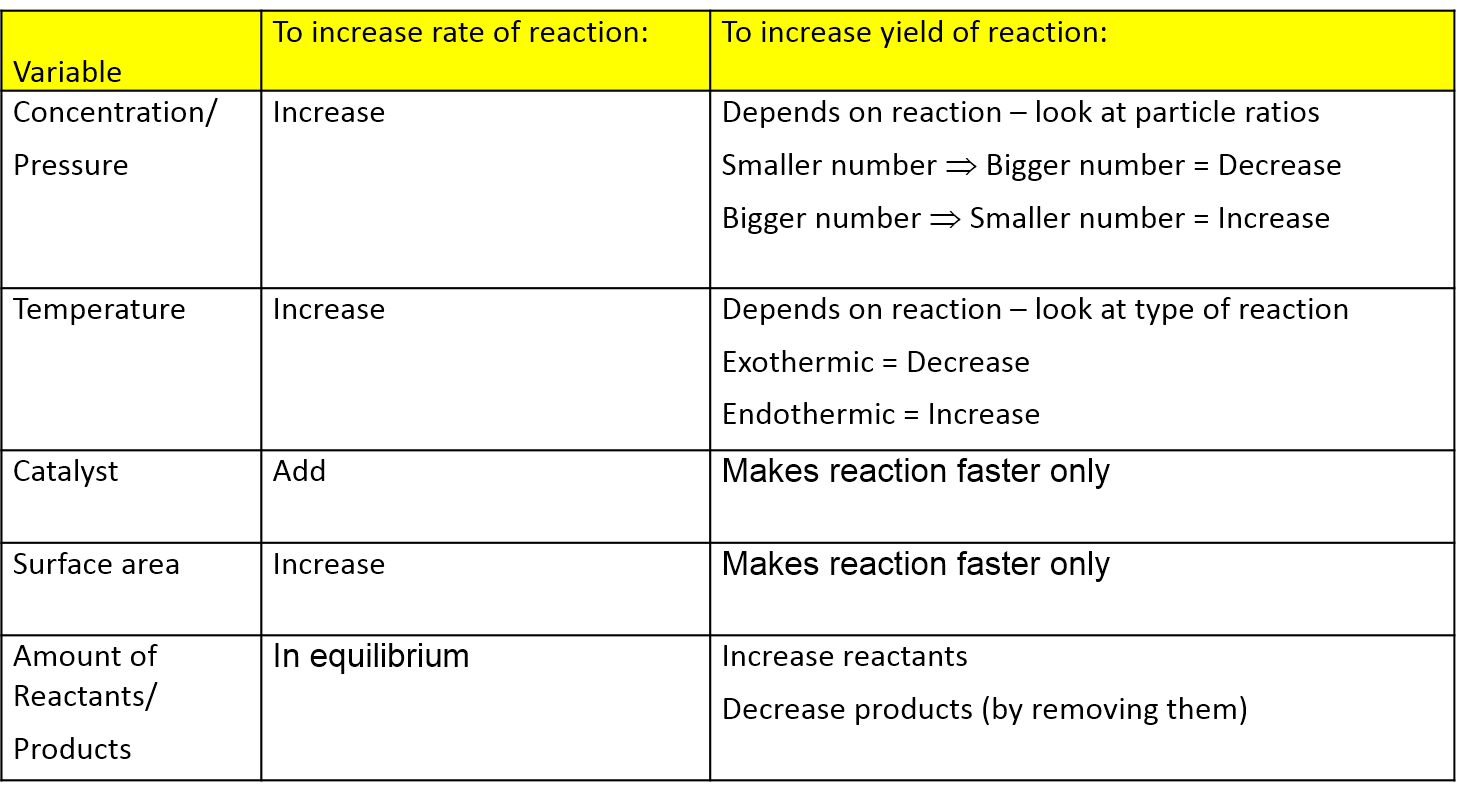
Le Chatelier S Principle Vce Chemistry
The product H CN diminishes more rapidly than does HCN.

. Higher Oxygen concentration B. Why does a candle burn more rapidly when placed in an open jar than in air. This same shift will result if some product HI is removed from the system which decreases the rate of the reverse reaction again resulting in the same imbalance in rates.
Catalysis will be discussed in greater detail later in this chapter as it relates to mechanisms of reactions. These rate laws are detailed below. Upon removal of products the rate of forward reaction becomes greater than that of backward reaction momentarily.
The rate of enzyme reaction is measured by the amount of substrate changed or amount of product formed during a period of timeThe rate is determined by measuring the slope of the tangent to the curve in the initial stage of the reaction. The rate of a reaction decreases as time progresses. Shift to left due to increase in Cl concentration.
AgCls Ag aq Cl aq some NaCl is added to the solution. Effect of Concentration Change on Equilibrium. An increase in the concentration of reactants 2.
The presence of a catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. This is usually done by cooling the reaction mixture so that NH 3 l condenses out. An increase in temperature 3.
At the same time the odds that the products will meet increase which increases the rate of the reverse reaction. The steeper the slope the greater is the rateIf enzyme activity is measured over a period of time the rate of reaction usually falls. Some enzymes are activated by different ways.
Removal of inhibitory peptide converts inactive forms of the enzyme zymogen or proenzyme to the active forms. Catalysts eg enzymes lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction and increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Increasing the surrounding temperature D.
Thus the catalyst is considered not to react. Is a substance that increases the speed of a reaction. Then more N 2 g and H 2 g are added and the reaction mixture is recycled to a condition of sufficiently high temperature that the rate becomes appreciable.
Convert the reactant to a single product 15. - when you stirmix the reactants can increase rate of reaction - it ensures reactants are kept in contact by removing build-up of products around reactants Example of Agitation. Catalysts work by increasing the frequency of collisions between reactants altering the orientation of reactants so that more collisions are effective reducing intramolecular bonding.
A catalyst increases the reaction rate by providing an alternative pathway or mechanism for the reaction to follow. Higher-energy collisions between reacting molecules A 1 and 2 only B 1 and 3 only C 2 and 3. In the case of temperature the value of the equilibrium has changed because the K eq is dependent on temperature.
4 Which of the following changes will increase reaction rate. You can increase reactant rate of a closed system Ie. Changes in concentration temperature and pressure can affect the position of equilibrium of a reversible reaction.
The reaction quotient Q C A B however does change immediately after the equilibrium is disturbed and with time converges to the same value as K e q once more. The role of a catalyst is to lower the activation energy so that a greater proportion of the particles have enough energy to. As a result the excess product will get converted to reactant.
As the generally favorable forward reaction is slower and the generally unfavorable reverse reaction is faster this equalizes them so that for every product formed theres one reactant formed per unit time. At equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction. This will depend on your choice of catalyst as well as reaction conditions however in general removal of ammonia will result in an increase in reaction rate based on the empirically derived rate laws.
That is why equilibria shift with changes in temperature. If reactant or product is removed the equilibrium shifts to make more reactant or product respectively to make up for the loss. -the equilibrium shifts toward the products.
Continuous removal of water vapor forces the reaction to the right so equilibrium is never achieved. What accounts for this reaction. Bon The equilibrium constant K e q C e q A e q B e q does not change upon addition or removal of species.
Activators increase the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Collision Theory tells us that the rate of reaction depends on the reactant particles colliding with energy in excess of the Activation Energy for the reaction. The catalyst does not increase the amount of production the catalyst only accelerates the reaction rate and is not included either as a reactant or as a product in the reaction.
Overall a catalyst is not a reactant and is not used up but it still affects how fast a. If the forward reaction is endothermic an increase in temperature causes. This is in accordance to Le Chateliers principle.
Form the bonds between the product molecules D. -the rate of the forward reaction increases to form more product until the system is again at equilibrium. C Removing the product NH 3 will shift the reaction to the right.
Closed container by increasing reactant concentration by injecting it or adding it in the container. The forward reaction is also favored by removing the products from the reaction mixture decrease in the concentration of products. When the product of a reaction at equilibrium is increased the equilibrium will shift left or to the reactant side.
The increase will cause more reactant particles to collide per unit volume and the proportion of fruitful or successful collisions will increase refer to collision theory Therefore Increaing rate of the. The system will experience a temporary net reaction in the forward direction to re-establish equilibrium the equilibrium will shift right. How Does A Catalyst Increase The Rate Of A Reaction A catalyst increases the rate of reaction in a slightly unconventional way from other means of increasing reaction rate.
HCNaq H aq CN aq the solution is diluted. As a reaction progresses the reactants are being turn junto the products so the number of reactant particles left is decreasing. Catalysts are widely used in the industry because they produce products faster thereby reducing costs.
Subsequently question is what affects equilibrium. The distinction is subtle but important and causes. Length of the candle.
A catalyst A substance that increases the speed of a reaction.

Factors That Affect Chemical Equilibrium Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts

No comments for "Does Removing Product Increase Reaction Rate"
Post a Comment